
Think of an organization where you go and take service and they are already ready with what you want and the way you want. Think of a shop or store you go and they receive you warmly and takes care of you till you buy products and even they call later and wants to know how they can make you happier and more satisfied. Have you ever felt a connection with any organization that the long you be with them you feel a very good feeling talking or keeping in touch with them just because they care for you. And that is want ISO 9001 international standard wants to have an organization.
This international standard specified requirements for a Quality Management System (QMS) where any organization wants to demonstrate its products and service to conform with the customer requirement, regulatory and statutory requirements and the organization’s own requirement. The present version of the standard ISO 9001:2015 is a very matured standard as ISO has declared it do not need any revision before 2030 whereas the previous standards were been revised in every 6-8 years duration.
Before diving down to compare how ISO 9001 can make your organization more sustainable first let’s get the idea what a sustainable business means.
Any business has two things to give a customer, a product or a service. Many organizations can give both. Before I explain this section, think of your organization where you work or if you are a student and don’t have a job or business, think of your father’s or mother’s company where he or she works in.
In common terms what we understand from the word “Sustainable Business” is a business which will sustain in the long run. The customers of the business should be happy the organization should maintain a consistency quality of its product or service. The internal employees should be happy and any interested parties of the organization should be satisfied with the organizations way of operating the business.

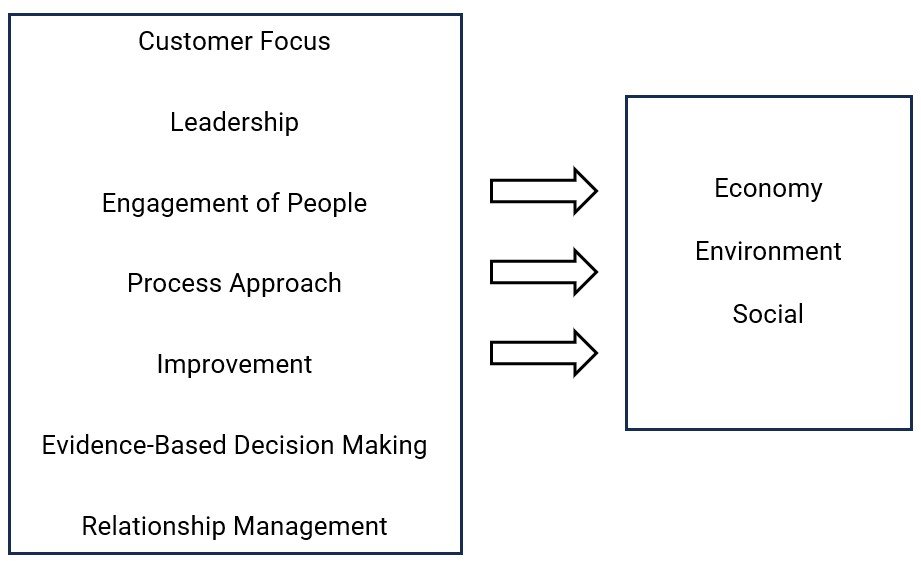
However, this idea needs a little maturity to understand what actually the word Sustainability means. For this we need to understand the pillars of sustainability. Sustainability has 3 pillars – i) Economy ii) Environment and iii) Social. By definition, sustainability is “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”. In other words, “the ability to continue something for a long time without harming the environment or people”.
On the other hand, the standard ISO 9001:2015 is based on 7 principles of Quality Management which are:
SafeBiz has brought a study relating each 7 principles of Quality Management System on which the international standard ISO 9001:2015 has been structured with the 3 pillars of sustainability explaining how this international standard can help your business make more sustainable:
Impact in Economy: A customer focused organization always outperforms competitors. When an organization focuses on customer and structures its operational process focusing customer satisfaction, the less important works are eliminated and the organization improves financially. When you focus on only the customer requirement, you will not do other activities which are not required by the customer. Many often organization thinks of a process is important or a product will do well and when it comes to market and do not perform well the time, money and effort are wasted. Customer focus will reduce your time in other less necessary works which you think is important but actually it is not.

Customer requirement changes from time to time. If an organization is customer focused, it will not suffer in getting new customers and the business will be going well with good sell. The reputation of the organization increases as well as the values of the products and service.
Customer focus not only reduces the time of less necessary works only but also focuses the organization in innovative idea of their product and service based on customer requirements. In such way the organization moves on and new product and service comes in the market. With a diversified market the economy changes drastically, market competition gets high and monopoly business gets down. Healthy competition takes place and the economic development of the country can be seen.

Impact in Environment: A customer-centric organization tends to prioritize not only the satisfaction of customer needs but also their growing demand for environmentally responsible practices. Now a days the customer is smarter than before. They are more aware of a product or service to buy if it is not been produced making negative impact to the environment. An ISO certified organization also will procure products or service from an environment friendly organization. Customers look for a product or service having less carbon footprint and less waste generation. For example, the RMG industries in Bangladesh are now more customer focused as it is a competitive market. The buyers also look for garments industries which in environment friendly other wise they do not give order. This impacted the garments factories to become more environment friendly. Even, the customers are ready to pay more for an ecofriendly product than other products. In the supply chain of any product or service, having a negative impact in the environment is now a days considered less tendency to be procured.
Impact in Social: A customer-focused organization has the potential to create substantial positive social impacts. By prioritizing customer satisfaction, organizations often extend their efforts to address broader social issues, aligning with the values and expectations of their customers.
Customer-focused organizations prioritize creating safe and high-quality products or services, ensuring the well-being of their customers and communities. Businesses design products or services that are inclusive and cater to diverse customer groups, including those with disabilities or from underserved areas.
A customer focused organization creates employment opportunity, provides training to the employees to ensure better customer service, arranges program for social responsibility and local community engagement, promotes diversity and inclusion, conducts ethical business practice, ensures health and safety etc. By embedding customer focus into organization’s core strategies, they not only enhance their competitiveness but also create meaningful social impacts that improve lives, foster equity, and contribute to sustainable societal progress.
Impact in Economy: Strong leaders develop strategies that drive innovation, improve operational efficiency, and increase market share, leading to higher profitability. Effective leadership ensures optimal allocation of financial and human resources, maximizing returns and reducing waste. Visionary leaders expand businesses, creating jobs and contributing to economic stability. They prioritize employee training and upskilling, enhancing workforce productivity and innovation.
Ethical leadership ensures adherence to regulations, resulting in consistent tax contributions to the government, which supports infrastructure and public services. They drive sustainable growth, boosting investor confidence and promoting economic stability in their sector.

Impact in Environment: A good leader understands the environmental impact of the organization and takes action accordingly. His/her commitment in the Environment Policy includes reduction of waste and carbon footprint as well as other environmental issues of the organization. They initiate prioritizing renewable energy and energy efficient processes. They are more likely to implement environmental compliances and follow ethical practice in the organization. Forward-thinking leaders implement recycling and reuse strategies, minimizing resource depletion. Their goal lies with border perspective of net-zero goal, SDG and contributes in the global climate change.
Impact in Social: Leadership significantly influences the social dynamics within and beyond an organization. Good leaders create inclusive cultures that ensure fair treatment and representation across gender, ethnicity, and abilities. They work to distribute resources equitably, addressing inequalities and reducing disparities within the organization and in the broader community. Through corporate social responsibility (CSR), effective leaders invest in community initiatives such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, directly improving quality of life. They aim to engage local stakeholders and foster positive relationships, recognizing the value of a supportive and happy community. In contrast, poor leadership can disrupt these efforts, undermining initiatives and damaging the organization’s social reputation. This underscores the importance of ethical and socially responsible leadership in maintaining a positive social impact.

Impact in Economy: Many organizations are significantly impacted when top management fails to communicate the mission and vision effectively to employees. Without proper engagement, financial setbacks occur. However, when employees are motivated and aligned with a common goal, organizations achieve success, improving economic conditions. This fundamental aspect, often overlooked in early stages, leads to long-term challenges. Engaged employees are motivated, focused, and aligned with objectives, driving productivity. They foster collaboration and innovation, identifying inefficiencies, reducing costs, and enhancing output. Such employees contribute ideas, driving innovation in products and services. Organizations with engaged workforces adapt quickly to market changes, maintaining competitiveness and gaining market share.


High levels of engagement reduce employee attrition, saving costs associated with recruitment, onboarding, and training. Engaged employees are more likely to show up and perform, reducing absenteeism-related costs and maintaining operational continuity. They work for customer satisfaction and remains loyal to the company.
Engaged employees contribute to achieving and often exceeding business targets, directly impacting revenue generation. By maximizing productivity, minimizing costs, and fostering customer loyalty, engagement helps to achieve healthier profit margins. Engaged employees enhance organizational resilience, contribute in positive employer branding, improves collaboration and knowledge sharing, aligns with strategic goals and ensures compliance and risk reduction.
The engagement of people in an organization is a vital driver of economic success. By fostering a culture of involvement, commitment, and collaboration, organizations can unlock their workforce’s full potential, resulting in higher productivity, reduced costs, sustained growth, and long-term profitability. Engaged people not only fuel internal economic stability but also position the organization as a leader in its industry, contributing to broader economic development.
Impact in Environment: During consulting various organizations we have seen how less engagement has impacted the environment management system of the organization. When the employees work together for a common goal, the chance of achieving it is very high. And when it comes to environment, it is not even a work for one employee or few. When everyone in an officer is aware of consuming less electricity, print minimum number of papers and generates less waste, only then drastic change can be seen.
Engaged employees are more likely to understand the importance of sustainability and adopt eco-friendly practices, both at work and in their personal lives. They conduct environmental aspect impact assessment and contributes in the environmental risk assessment. Employees and stakeholders actively champion green initiatives, raising awareness and influencing others to adopt sustainable behaviors. Engaged employees are more willing to environment friendly activities such as reducing waste, promoting resource efficiency, supporting green innovation, maintaining environmental compliances, creating a culture of sustainability, reducing carbon footprint, supporting circular economy practices and driving long term environmental goals.



Impact in Social: When employees feel valued, empowered, and deeply connected to their organization’s mission, vision, and values, it fosters a positive and inclusive work culture that drives both individual and collective success. This connection helps to strengthen relationships within the organization while also enhancing its engagement with the broader community, promoting social well-being and a sense of shared purpose. Engaged employees are more inclined to embrace diversity, advocate for inclusivity, and encourage equity, creating a harmonious and supportive workplace where everyone feels respected, appreciated, and motivated to contribute their best efforts. Such engagement boosts collaboration and mutual support among employees, leading to stronger interpersonal relationships, improved teamwork, and a heightened sense of community within the organization. Employees who are truly engaged experience higher levels of job satisfaction, which helps reduce workplace stress and enhances their overall mental and physical health. They are more motivated, resilient, and focused, often achieving a healthier and more sustainable work-life balance. This, in turn, drives both personal fulfillment and organizational success.
Engaged employees are more eager to participate in CSR activities and strengthens community relations. This goes a long way in social sustainability as the reputation of the organization sky rockets. The engaged employees act like an advocate for the organization’s values, positively influencing the public perception of the company. Engaged employees promote and respect cultural diversity, ensuring fair treatment for individuals from different backgrounds. A high-engagement culture often includes initiatives to combat bias, harassment, and inequality in the workplace, promoting fairness and social justice. Engaged employees promotes ethical practices (i.e. fair labor practice, equal treatment), supports social innovations (i.e. creative ideas, education) and ethical practice in supply chains.
Impact in Economy: The process approach is a management strategy that emphasizes understanding, controlling, and improving processes within an organization to achieve desired outcomes efficiently and effectively. When implemented, this approach can significantly impact the economic performance of an organization by improving productivity, reducing costs, and enhancing overall profitability. It is obvious that if an organization specifies its processes and define the input, activities and output and conduct the operation accordingly, less waste will be produced, the operation will have less operating cost and the system will be efficient. This will result in financial benefits to the organization. The process approach ensures minimum resources are used as an input and maximum output can be found. The implementation of a process approach drives economic performance by optimizing resources, reducing costs, and enhancing productivity. This strategic focus on efficiency and quality positions organizations for long-term profitability and growth while contributing to national and global economic development.


Impact in Environment: When the operation of an organization follows process approach the productivity increases and less waste is generated. This impacts on the environment positively. Working deeply the in-process approach sometimes reduces the carbon footprint as well. Because less power consumption reduces as well as specific machines or equipment are operated only. The pollution also reduces and sustainable supply chain is implemented.
The lifestyle thinking in product design impacts in the environment and impact in biodiversity is assessed. Process approach promotes environmental compliance and the employees also follow process wise environmental aspect and impact assessment. Process wise environmental aspect impact assessment ensures all the activities are covered and the operation is environment friendly.
Impact in Social: When applied to social dimensions, this approach fosters a structured framework for improving employee well-being, fostering community engagement, and promoting equitable practices. Systematic activities for social responsibility can go a long way. It creates a good reputation in the community and the organization’s CSR activities are accepted warmly.
A process-driven approach identifies inefficiencies or hazards in the workplace, leading to safer and healthier environments for employees. Conducting regular training to the community helps organization to identify the gaps in knowledge and awareness. This gives an idea how the awareness can be developed in different social aspects to the community. Regular survey to the community and stakeholders helps to identify the needs and expectations of them to the organization.

Defined processes provide employees with clear expectations and responsibilities, empowering them to contribute effectively. Training and development become systematic, ensuring employees gain the skills needed to grow professionally. A structured approach ensures recognition systems are fair and consistent, boosting morale and motivation.
Improvement is not a defined strategy by using an organization can have specific impact on economy, environment and social. It’s a requirement for the QMS which carries the organization to keep on changing and developing their product and service. So, in this section no strategic study can be carried out.
Impact in Economy: Evidence-based decision-making (EBDM) involves using data, research, and factual evidence to guide strategies and actions within an organization. It reduces reliance on intuition or assumptions, leading to informed and effective decisions. The evidence-based decision making helps organization to have some economic impact. For example, when organization evidence-based decisions are made, organization does very small number of mistakes as the data which are coming are from facts. When the decisions are made from a forecasted data, in that case the chances for mistake would have been high. Any decision for financial or economy of the organization can be benefited if the decisions are taken based on real facts and evidence based.

Impact in Environment: Evidence-based decision-making (EBDM) can significantly impact an organization’s environmental performance and sustainability by providing a structured approach to integrating data, facts, and analysis into operational and strategic choices. By analyzing resource usage data (e.g., energy, water, raw materials), organizations can identify inefficiencies and implement measures to minimize waste. Monitoring energy consumption can lead to upgrading to energy-efficient machinery, reducing carbon footprint. EBDM helps organizations stay compliant with environmental regulations by using data to anticipate potential risks and rectify issues early. Decisions based on life-cycle assessments (LCA) and environmental impact studies enable organizations to select sustainable alternatives in production and operations. For example, transitioning to biodegradable packaging after studying its impact on waste streams can lead to better sustainability.
EBDM supports creating realistic and impactful sustainability goals, such as achieving net-zero emissions by analyzing historical and predictive environmental data. For example, using predictive analytics to model the impact of renewable energy adoption on carbon reduction targets. Sharing evidence-based environmental achievements builds trust with stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and investors. Reporting GHG emissions reduction using verified data aligns with global sustainability frameworks, such as the GRI or CDP is a good example.
Impact in Social: Evidence-based decision-making can significantly impact the social aspects of an organization by fostering inclusivity, enhancing employee satisfaction, strengthening community engagement, and ensuring accountability. Analyzing workforce demographics and recruitment data, biases and implement inclusive hiring policies can be identify. Evidence-based metrics for performance evaluation reduce favoritism and ensure equal opportunities for advancement. Employee surveys and health assessments provide actionable insights to address mental health issues, workplace safety concerns, and overall well-being. Monitoring absenteeism and turnover rates can help tailor policies, such as flexible work hours or better health benefits, to meet employee needs.


Impact in Economy: There are many impacts of the relationship management in economy. Healthy relationships with customers and suppliers foster loyalty and ensure smooth operations, reducing disruptions and improving profitability. Collaboration with financial institutions and investors strengthens access to funding for growth and innovation. Working closely with supply chain partners can streamline processes, reduce waste, and lower costs, leading to better economic outcomes. Having a good stakeholder relationship can build a positive brand image, attract customers, investors, and talent, which can contribute to economic stability and growth. Collaborating with communities and governments to create shared economic value ensures long-term benefits for all parties, such as job creation, infrastructure development, and market expansion.
Impact in Environment: Having a good relation with suppliers and customers can promote the adoption of green practices, such as sustainable sourcing, waste reduction, and recycling programs. Engaging with regulators and environmental groups ensures compliance with environmental laws and facilitates access to innovations like renewable energy or eco-friendly technologies. Strong internal relationships enable organizations to promote environmental awareness among employees and stakeholders, fostering responsible behaviors like energy conservation and waste management. Long-term relationships with supply chain partners can help set and achieve mutual sustainability objectives, such as carbon footprint reduction.


Impact in Social: Positive workplace relationships boost morale, improve retention, and encourage a collaborative culture. Employees who feel valued are more likely to engage in CSR activities and advocate for the organization’s social initiatives. Strong ties with local communities enable organizations to identify and address their specific needs, such as education, healthcare, or infrastructure development. Collaborative efforts with NGOs and local groups amplify the impact of social programs. Transparent communication and ethical practices strengthen relationships with stakeholders, enhancing trust and ensuring social responsibility.
This alignment with the principals of QMS with Sustainable pillars is a vast topic which can have a huge scope for further study and research.
Some similar studies can be found in the journal paper: “An Integrated Sustainable Quality Management Framework for Quality-Related Research” by Adeeb A. Kutty, Galal M. Abdella, Murat Kucukvar.